This transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation; both the left and right sides of the equation increase by +$250. For example, if a company becomes bankrupt, its assets are sold and these funds are used to settle its debts first. Only after debts are settled are shareholders entitled to any of the company’s assets to attempt to recover their investment. On the other hand, equity refers to shareholder’s or owner’s equity, which is how much the shareholder or owner has staked into the company.
- Before taking this lesson, be sure to be familiar with the accounting elements.
- We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect and to demonstrate the cumulative effect on the accounting equation.
- As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change.
- The merchandise would decrease by $5,500 and owner’s equity would also decrease by the same amount.
What Are the 3 Elements of the Accounting Equation?
If assets increase, either liabilities or owner’s equity must increase to balance out the equation. Since the balance sheet is founded on the principles of the accounting equation, this equation can also be said to be responsible for estimating the net worth of an entire company. The fundamental components of the accounting equation include the calculation of both company holdings and company debts; thus, it allows owners to gauge the total value of a firm’s assets. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. A company’s liabilities include every debt it has incurred.
Effects of Transactions on the Accounting Equation
Metro Corporation paid a total of $1,200 for utility bill. Metro Corporation paid a total of $900 for office salaries. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
The relationship between the accounting equation and your balance sheet
Assets in accounting are resources that a company owns and uses to generate income and future economic benefits. Examples of assets are company equipment, vehicles, accounts what is a accounts receivable journal entry receivable (A/R), prepaid insurance, and office supplies. They can be classified as operating or nonoperating, tangible or intangible, and current or noncurrent.
What if any one of these elements changes?
The accounting equation nonetheless always stays in balance. Under the double-entry accounting system, each recorded financial transaction results in adjustments to a minimum of two different accounts. The accounting equation sets the foundation of “double-entry” accounting, since it shows a company’s asset purchases and how they were financed (i.e. the off-setting entries). When a company purchases goods or services from other companies on credit, a payable is recorded to show that the company promises to pay the other companies for their assets.
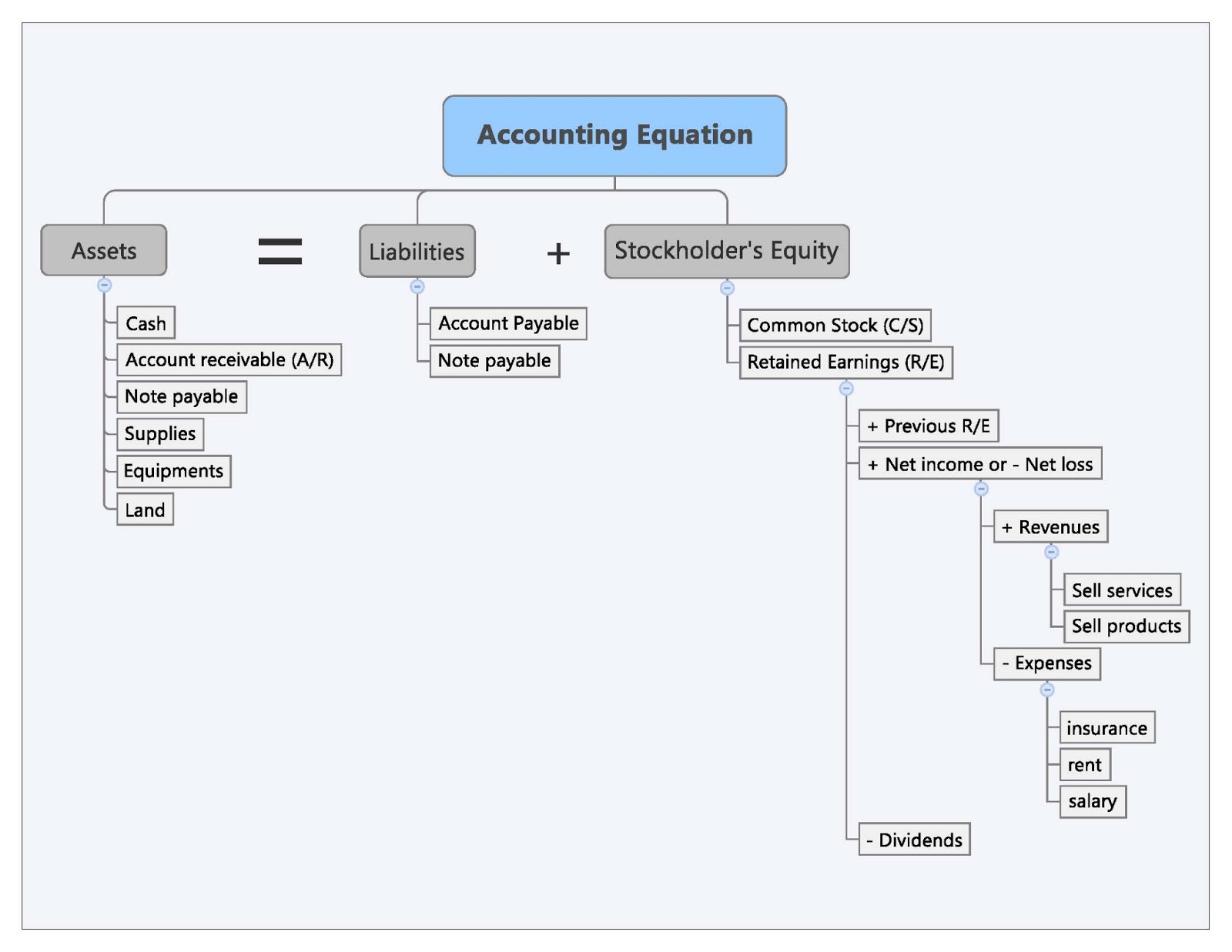
Components of the Equation
It is sometimes called net assets, because it is equivalent to assets minus liabilities for a particular business. ” The answer to this question depends on the legal form of the entity; examples of entity types include sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. A sole proprietorship is a business owned by one person, and its equity would typically consist of a single owner’s capital account. Conversely, a partnership is a business owned by more than one person, with its equity consisting of a separate capital account for each partner. Finally, a corporation is a very common entity form, with its ownership interest being represented by divisible units of ownership called shares of stock. Corporate shares are easily transferable, with the current holder(s) of the stock being the owners.
On 22 January, Sam Enterprises pays $9,500 cash to creditors and receives a cash discount of $500. For every business, the sum of the rights to the properties is equal to the sum of properties owned. To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline. Parts 2 – 6 illustrate transactions involving a sole proprietorship.Parts 7 – 10 illustrate almost identical transactions as they would take place in a corporation.Click here to skip to Part 7.
So some common current liabilities like you see here is accounts payable. We had an invoice and we’ve got to pay that invoice to them. If we took out a loan that we’re going to pay back in less than a year, just a short term kind of keep our money flowing, well that would be a current liability. Compare that with a long term liability which is payable in over 1 year, right? And these are going to be things like long term loans when we get a bank loan or bonds.

